Running the Deployment
As we saw in previous sections, clusters are deployed using the ZTP GitOps Pipeline, but before starting we need to load it into our hub cluster.
We already have the Git repository that will be used for storing our Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Configuration as Code (CaC). Next step is deploying the ZTP GitOps Pipeline, let’s do it.
| Below commands must be executed from the workstation host if not specified otherwise. |
Before continuing, make sure you have the following tooling installed in your workstation:
Deploying the ZTP GitOps Pipeline
In the workstation, run the following command to extract the pipeline installation files:
If you get ERRO[0000] running `/usr/bin/newuidmap 51706 0 1000 1 1 100000 65536: newuidmap: write to uid_map failed: Operation not permitted` when running podman commands, run them with sudo.
|
mkdir -p ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/
podman login infra.5g-deployment.lab:8443 -u admin -p r3dh4t1! --tls-verify=false
podman run --log-driver=none --rm --tls-verify=false infra.5g-deployment.lab:8443/openshift4/ztp-site-generate-rhel8:v4.12.3-3 extract /home/ztp --tar | tar x -C ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/Now that we extracted the pipeline content we need to get it applied to our hub cluster:
-
Login into the hub cluster.
The command below must be changed to use the OpenShift admin password provided in the e-mail you received when the lab was ready. oc --kubeconfig ~/5g-deployment-lab/hub-kubeconfig login -u admin -p <admin_password> https://api.hub.5g-deployment.lab:6443 --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true -
Modify the ZTP GitOps Pipeline configuration to match our environment configuration.
-
Change the repository url for the two ArgoApps:
sed -i "s|repoURL: .*|repoURL: http://infra.5g-deployment.lab:3000/student/ztp-repository.git|" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/clusters-app.yaml sed -i "s|repoURL: .*|repoURL: http://infra.5g-deployment.lab:3000/student/ztp-repository.git|" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/policies-app.yaml -
Change the repository path for the two ArgoApps:
sed -i "s|path: .*|path: site-configs|" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/clusters-app.yaml sed -i "s|path: .*|path: site-policies|" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/policies-app.yaml -
Change the repository branch for the two ArgoApps:
sed -i "s|targetRevision: .*|targetRevision: main|" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/clusters-app.yaml sed -i "s|targetRevision: .*|targetRevision: main|" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/policies-app.yaml
-
-
Allow
ClusterImageSetresource to the list of allowed resources:sed -i "/clusterResourceWhitelist:/a \ \ - group: \'hive.openshift.io\'\n \ \ \ kind: ClusterImageSet" ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/app-project.yaml -
Apply the ZTP GitOps Pipeline configuration:
oc --kubeconfig ~/5g-deployment-lab/hub-kubeconfig apply -k ~/5g-deployment-lab/ztp-pipeline/argocd/deployment/
Deploying the SNO Cluster using the ZTP GitOps Pipeline
When we applied the ZTP GitOps Pipeline configuration in the last section, that created two ArgoCD apps. One of the apps (clusters) take care of deploying the clusters defined in the SiteConfig while the other (policies) take care of deploying the policies defined in the different PolicyGenTemplates.
Since the apps have been created, ArgoCD started doing its magic which means that the cluster deployment should already be running, let’s see what happened in Argo CD.
-
Login into Argo CD.
-
When accessing choose
Logging with OpenShift, on the next screen use the OpenShift Console Admin credentials. -
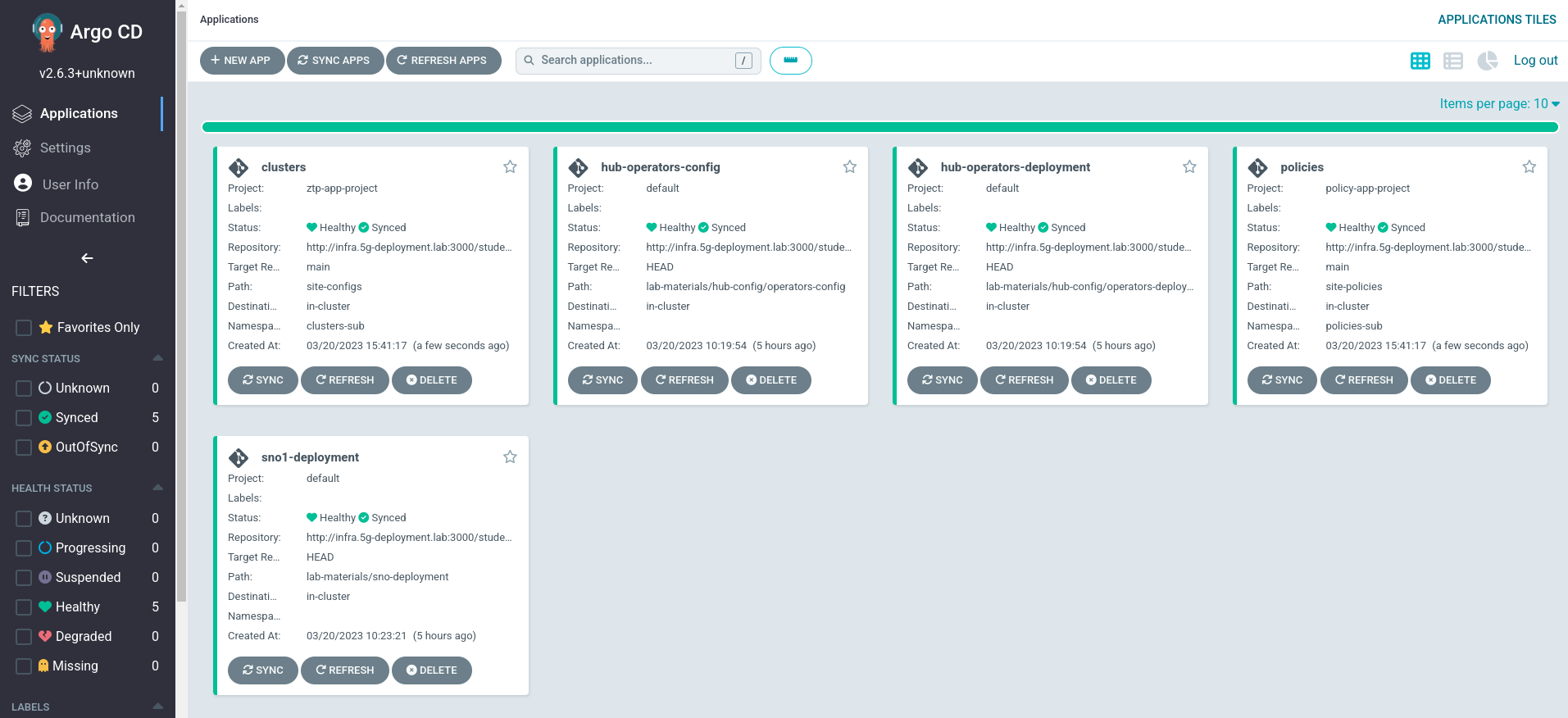
You will see the follow applications:
-
From all these apps, the ones related to the ZTP GitOps Pipeline are
clustersandpolicies. If we click onclusterswe will see the following screen: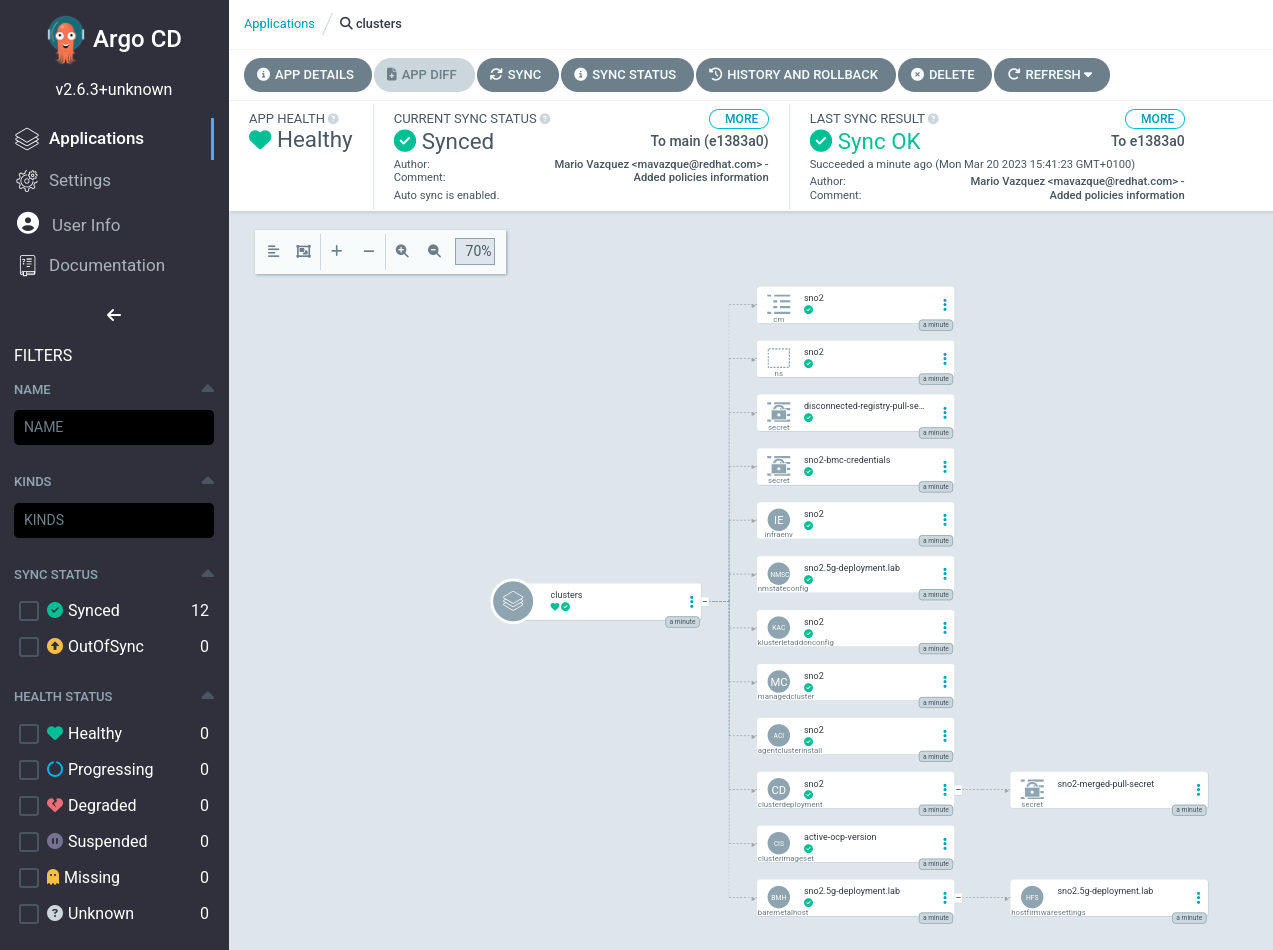
-
You can see how the pipeline created all the required objects to get our site deployed.
-
If we check the
policiesapp this is what we will see: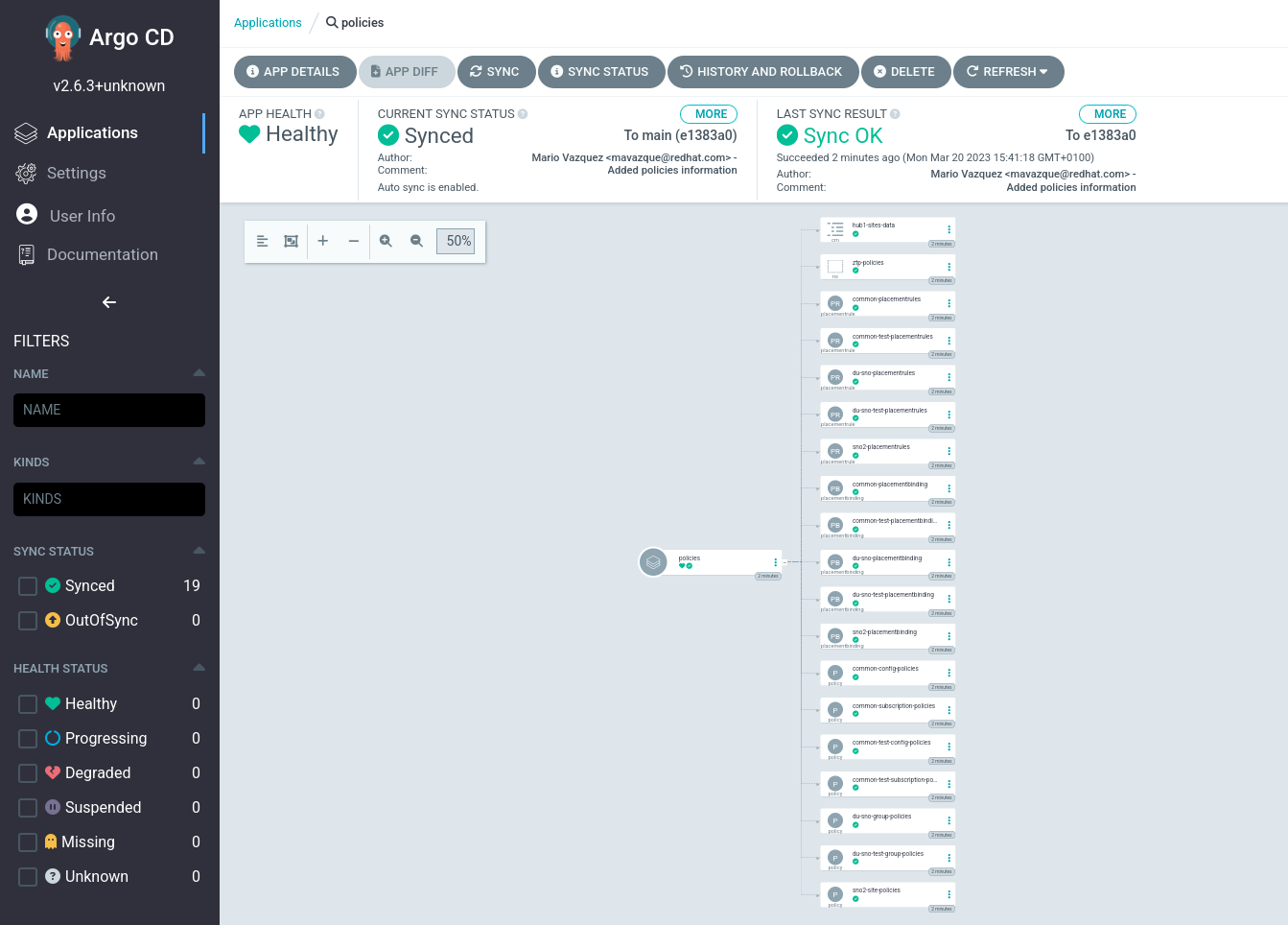
In the next section we will see how we can monitor the deployment process.